Are you frustrated with your seemingly endless struggle to gain weight? Despite your efforts, the numbers on the scale refuse to budge and you’re left wondering why. In this article, we will explore the possible reasons behind your inability to put on pounds and provide you with practical tips to help you achieve your goal. Whether you’re an ectomorph trying to bulk up or simply looking to add a few pounds to your frame, we’ve got you covered. So, let’s dive into the factors that might be hindering your weight gain and discover effective strategies to overcome them.
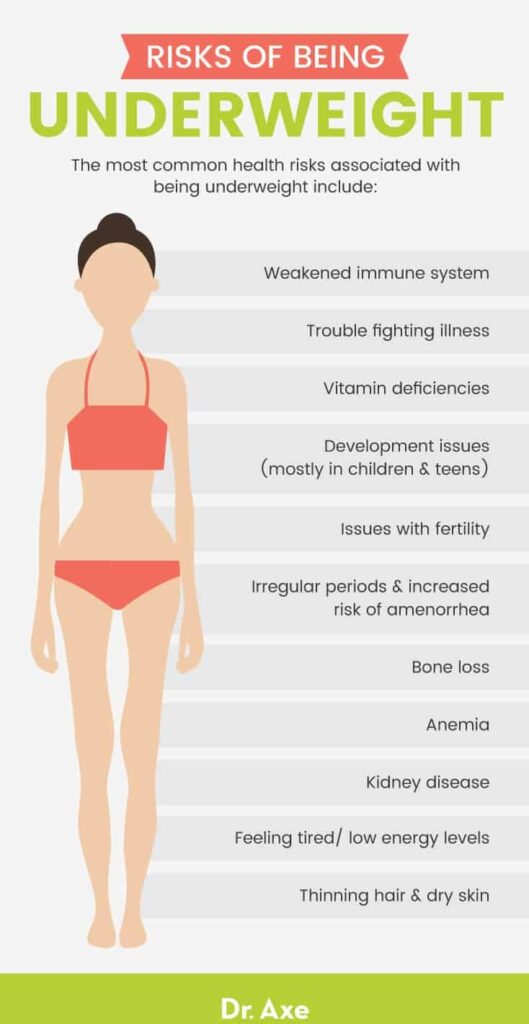
Possible Medical Conditions
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a medical condition in which your thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating your metabolism. When your thyroid glands produce too much of these hormones, it can lead to an increased metabolic rate, making it difficult for you to gain weight. If you suspect that hyperthyroidism may be the cause of your weight struggles, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the body’s inability to tolerate gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Individuals with celiac disease often experience damage to the lining of their small intestine when they consume gluten. This damage can affect the absorption of nutrients, including calories, which can contribute to difficulty in gaining weight. If you suspect that you may have celiac disease, it is important to undergo testing and work with a healthcare professional to manage the condition through a gluten-free diet.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term used to describe chronic inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These conditions can cause inflammation and damage to the digestive system, leading to nutrient malabsorption and weight loss. While weight loss is a common symptom, some individuals with IBD may also struggle with gaining weight due to the overall impact on their digestive system. Managing IBD through medication, dietary modifications, and regular monitoring by a healthcare professional is crucial in addressing weight struggles.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Various gastrointestinal disorders such as gastroparesis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can impact your ability to gain weight. Gastroparesis is a condition characterized by delayed stomach emptying, causing a feeling of fullness and difficulty in consuming enough calories. IBS and GERD can also lead to reduced food intake and nutrient absorption. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to properly diagnose and manage gastrointestinal disorders to improve weight gain and overall digestive health.
Diabetes
While diabetes is commonly associated with weight gain, some individuals with diabetes may struggle to gain weight. Uncontrolled diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, can lead to weight loss due to the body’s inability to properly utilize glucose for energy. Additionally, certain diabetes medications can affect appetite and metabolism, further contributing to weight struggles. It is essential to work with a healthcare professional to manage diabetes effectively and address weight concerns specific to your condition.
Malabsorption Issues
Malabsorption issues can occur due to various underlying factors such as gastrointestinal disorders, food intolerances, or nutrient deficiencies. Conditions like lactose intolerance, gluten intolerance, and deficiencies in certain enzymes may impact the absorption of nutrients, leading to weight struggles. A healthcare professional can help identify the specific causes of malabsorption and provide guidance on dietary modifications and potential supplementation to support proper nutrient absorption and weight gain.
Food Allergies or Sensitivities
Food allergies or sensitivities can trigger an immune response in the body, causing symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe reactions. These reactions can affect your ability to consume and fully absorb certain foods, leading to potential weight struggles. Common allergens such as dairy, eggs, nuts, and shellfish can be culprits. If you suspect food allergies or sensitivities are contributing to your weight concerns, it is crucial to undergo the necessary testing and work with a healthcare professional to effectively manage your diet and address any nutrient deficiencies.
High Metabolism
Understanding Metabolism
Metabolism refers to the processes in your body that convert food into energy. It is influenced by various factors and can vary from person to person. While some individuals naturally have a higher metabolic rate, others may experience a slower metabolism. Understanding your metabolism can help you better comprehend how it affects your weight struggles and find strategies to address them effectively.
Factors Affecting Metabolism
Several factors can influence your metabolism, including age, gender, body composition, and activity level. As we age, our metabolism tends to slow down. Men usually have a higher metabolic rate than women due to differences in hormone levels and body composition. Additionally, individuals with a higher proportion of muscle mass generally have a higher metabolism compared to those with a higher percentage of body fat. Lastly, physical activity and exercise can increase your metabolic rate, allowing you to burn more calories even at rest.
Ways to Boost Metabolism
If you have a naturally high metabolism or want to increase your metabolic rate to aid in weight gain, there are several strategies you can try. Regular exercise, particularly strength training exercises, can help build and maintain muscle mass, which can increase your metabolism. Consuming small, frequent meals throughout the day can also help keep your metabolism active. Additionally, ensuring you are getting enough protein in your diet can promote muscle growth and support a healthy metabolism. Finally, staying hydrated and getting enough quality sleep are essential for maintaining a balanced metabolism.
Inadequate Caloric Intake
How Many Calories Do You Need?
The number of calories you need depends on various factors, including your age, gender, height, weight, activity level, and overall goals. To assess your caloric needs accurately, it is recommended to consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional who can evaluate your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations. In general, consuming more calories than your body burns is necessary for weight gain.
Dietary Requirements for Weight Gain
When aiming to gain weight, it is crucial to focus on consuming a balanced and nutrient-dense diet. Including a variety of whole foods such as lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help provide the necessary energy and essential nutrients to support weight gain. Incorporating calorie-dense foods like nuts, nut butter, avocados, and oils can also be helpful in boosting your caloric intake.
Eating Enough Protein
Protein plays a vital role in supporting weight gain and muscle growth. Including adequate protein in your diet is essential for repairing and building tissues. Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Aim to include protein-rich foods with each meal and snack to ensure you are meeting your protein requirements.
Enjoying Calorie-Dense Foods
To increase your caloric intake, incorporating calorie-dense foods into your meals and snacks can be beneficial. Foods such as whole milk, cheese, whole-grain bread, dried fruits, granola, and nut butter are examples of calorie-dense options. It is important to note that while these foods can contribute to weight gain, they should still be consumed as part of a balanced diet to ensure you are getting the necessary nutrients from a variety of sources.
Lack of Muscle Mass
Effects of Lack of Exercise on Weight Gain
Lack of exercise can contribute to difficulties in gaining weight, especially when it comes to building lean muscle mass. Regular exercise, especially resistance training, is crucial for stimulating muscle growth and increasing muscle mass. Without exercise, your body may be more prone to storing excess calories as fat rather than building muscle, which can lead to an unhealthy weight distribution and overall body composition.
Resistance Training for Muscle Growth
Incorporating resistance training into your exercise routine is essential for promoting muscle growth and weight gain. Exercises such as weightlifting, bodyweight exercises, and resistance band workouts can help stimulate muscle development. It is important to start with an appropriate weight or resistance level and gradually increase over time to challenge your muscles and encourage growth.
Importance of Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are often overlooked aspects of a successful weight gain journey. Adequate rest allows your muscles to repair and grow stronger. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support optimal recovery. Additionally, incorporating rest days into your exercise routine is crucial for preventing overtraining and reducing the risk of injury. Listen to your body and give it the time it needs to recover and build muscle effectively.
Creating an Effective Workout Routine
When creating a workout routine for weight gain, it is important to focus on both resistance training and aerobic exercises. Resistance training should be prioritized to stimulate muscle growth, while aerobic exercises can be included to promote cardiovascular health and overall fitness. Consistency is key, so aim to exercise at least 3-4 times a week, allowing for proper rest and recovery in between sessions. Consulting with a qualified fitness professional can help you design a personalized workout routine that aligns with your weight gain goals and physical abilities.

Psychological Factors
Stress and Weight Gain
Stress can have significant impacts on our overall well-being, including our body weight. When we experience stress, the body releases stress hormones such as cortisol, which can influence our appetite and metabolism. Some individuals may experience increased cravings for high-calorie comfort foods as a response to stress, leading to weight gain. Additionally, chronic stress can disrupt sleep patterns and hinder motivation for exercise, further affecting weight management.
Emotional Eating Habits
Emotional eating refers to the consumption of food in response to emotions rather than physical hunger. It is a common coping mechanism for individuals facing emotional distress or seeking comfort. Emotional eating can lead to weight gain as it often involves the consumption of calorie-dense foods that may not be nutritionally balanced. Developing healthier coping strategies such as mindfulness, physical activity, or seeking support from loved ones can help break the cycle of emotional eating and support overall weight management.
Body Image Issues
Body image concerns can greatly impact our perception of weight and contribute to struggles in gaining weight. Negative body image often goes hand in hand with low self-esteem, and individuals may engage in unhealthy behaviors such as restrictive diets or excessive exercise to achieve an idealized body shape or size. It is crucial to prioritize positive body image and focus on overall health and well-being rather than societal ideals. Seeking support from mental health professionals or engaging in body-positive communities can be helpful in fostering a healthier relationship with your body and addressing weight concerns.
Impact of Mental Health on Weight
Mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and eating disorders can significantly affect our relationship with food and body weight. These conditions can amplify stress responses, disrupt healthy eating patterns, and contribute to disordered eating behaviors. Seeking professional help and a comprehensive approach that addresses both mental health and weight concerns is essential in overcoming these challenges. Working with mental health professionals and registered dietitians trained in the treatment of eating disorders can provide the necessary support and guidance on the path to recovery.
Side Effects of Medications
Common Medications Affecting Weight
Certain medications may have an impact on your weight, either by increasing or decreasing appetite, altering metabolism, or affecting nutrient absorption. Medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, corticosteroids, and some hormonal contraceptives have been associated with weight gain or difficulty in losing weight. If you suspect that your medication is affecting your weight, it is important to consult with the prescribing healthcare professional to discuss any potential alternatives or adjustments in your treatment plan.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
When experiencing weight struggles due to medication side effects, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action. They can evaluate your medication regimen, consider potential alternatives or adjustments, and help develop a comprehensive plan to support healthy weight management. It is important to never discontinue or adjust medication without professional guidance.
Alternative Medication Options
In some cases, healthcare professionals may be able to offer alternative medication options that have different side effect profiles. These alternatives may have lesser impacts on weight or even promote weight gain, depending on the specific needs and health conditions of the individual. It is important to have open and honest communication with your healthcare professional to explore available options that can effectively address your medical condition while minimizing unwanted effects on weight.
Eating Disorders
Anorexia Nervosa
Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight, severe restriction of food intake, and a distorted perception of body weight and shape. Individuals with anorexia nervosa often have a significantly low body weight and struggle to maintain or gain weight. This serious mental health condition requires specialized treatment from a multidisciplinary team consisting of mental health professionals, registered dietitians, and medical doctors to address both the physical and psychological aspects of the disorder.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by a cycle of binge-eating episodes followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-induced vomiting, excessive exercise, or the misuse of laxatives or diuretics. The binge-eating episodes often involve consuming large quantities of high-calorie foods, but the subsequent compensatory behaviors can make it challenging for individuals to gain weight. Treatment for bulimia nervosa typically involves therapy, nutritional counseling, and medical support to address the underlying factors contributing to the disorder.
Binge Eating Disorder
Binge eating disorder (BED) is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of consuming large quantities of food without the use of compensatory behaviors typically seen in bulimia nervosa. Individuals with BED often experience a lack of control during binge-eating episodes and may consume food rapidly until they are uncomfortably full. While weight gain is commonly associated with binge eating disorder, it is important to note that individuals may have varying weight statuses. Treatment for BED often involves psychotherapy, support groups, and nutritional counseling to address the emotional, behavioral, and nutritional aspects of the disorder.
Seeking Professional Help
Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that require professional assessment and treatment. If you suspect that you may have an eating disorder or struggle with disordered eating patterns, it is crucial to reach out to a healthcare professional who specializes in eating disorders. They can provide an accurate diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and offer ongoing support throughout your recovery journey.
Malnutrition
Causes of Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when the body does not receive adequate nutrients to support optimal health. It can be caused by various factors, including inadequate food intake, poor dietary choices, underlying medical conditions, or a combination of these factors. Neglecting proper nutrition can lead to weight loss and overall poor health. Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of malnutrition is essential for regaining weight and improving nutritional status.
Effects on Weight and Health
Malnutrition can have significant impacts on weight and overall health. Inadequate intake of calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals can lead to severe weight loss, muscle wasting, weakened immune system, impaired wound healing, fatigue, and decreased organ function. Additionally, malnutrition increases the risk of developing other medical complications, further compromising one’s well-being. It is important to seek medical and nutritional support to prevent and address malnutrition effectively.
Improving Nutritional Status
Improving nutritional status requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both the quantity and quality of one’s diet. Consulting with a registered dietitian can provide personalized nutrition guidance and support. It is important to focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including lean proteins, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Supplementation may be necessary in certain cases where nutrient deficiencies are present. Consistency and regular monitoring of nutritional intake are key to improving nutritional status and achieving healthy weight gain.

Inadequate Sleep
Role of Sleep in Weight Regulation
Getting adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Sleep plays a significant role in regulating various hormones that influence appetite and metabolism. Sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of these hormones, leading to increased hunger, decreased satiety, and alterations in energy expenditure. These hormonal changes can make it challenging to regulate food intake and may contribute to weight struggles.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation
Lack of sleep can have several negative effects on weight management. Sleep-deprived individuals often experience increased cravings for high-calorie, carbohydrate-rich foods. This, combined with decreased impulse control and heightened hunger sensations, may contribute to overeating and weight gain. Additionally, sleep deprivation can disrupt the body’s ability to properly process carbohydrates, leading to impaired glucose metabolism and an increased risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Tips for Better Sleep
Establishing healthy sleep habits is essential for improving both the quantity and quality of your sleep. Here are some tips that can help promote better sleep:
- Stick to a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time each day.
- Create a sleep-conducive environment by keeping your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Prioritize relaxation and wind-down activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing mindfulness techniques.
- Limit exposure to electronic devices, particularly blue light, before bed as it can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Avoid consuming caffeine or stimulants close to bedtime.
- Engage in regular physical activity, but avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime.
- Develop a bedtime routine that signals your body it’s time to sleep, such as practicing light stretching, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Implementing these tips into your routine can help create a conducive environment for quality sleep, allowing your body to regulate hormones, support weight management, and overall well-being.
Underlying Genetic Factors
Genetic Predisposition to Low Weight
Genetics can play a role in an individual’s natural body weight, metabolism, and ability to gain weight. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to a lower weight, making it more challenging for them to gain weight compared to others. While genetic factors can influence weight, it is important to remember that they are just one piece of the puzzle, and lifestyle factors, such as diet and physical activity, can still play a significant role in achieving weight goals.
Understanding Your Genetic Makeup
Understanding your genetic makeup can provide useful insights into how your body processes and responds to certain foods and exercise. Genetic testing services are available that can provide information about your unique genetic variants related to metabolism, nutrient absorption, and other factors that may impact weight management. By knowing this information, you can make more informed choices about your diet and exercise routines that align with your individual genetic profile.
Working with Genetic Counselors
If you choose to pursue genetic testing or want to understand your genetic predisposition better, working with a genetic counselor can be beneficial. Genetic counselors are healthcare professionals with expertise in genetics who can help interpret the results of genetic testing and provide guidance on how it may impact various aspects of your health, including weight management. They can also provide personalized recommendations and support in addressing any concerns related to your genetic predisposition and weight struggles.
In conclusion, struggling to gain weight can stem from various factors, including medical conditions, high metabolism, inadequate caloric intake, lack of muscle mass, psychological factors, side effects of medications, eating disorders, malnutrition, inadequate sleep, and underlying genetic factors. Understanding each potential cause can provide valuable insights in addressing weight concerns effectively. It is important to seek professional guidance from healthcare providers, registered dietitians, mental health professionals, and genetic counselors as needed to develop a comprehensive plan tailored to your individual needs. Remember, gaining weight in a healthy and sustainable manner requires patience, consistency, and a holistic approach that promotes overall well-being.
