Are you curious about whether you are underweight? It’s essential to have a clear understanding of your body weight and if it falls within a healthy range. Discovering if you are underweight involves more than simply stepping on a scale. There are various factors to consider, such as your Body Mass Index (BMI), body composition, and overall health. By evaluating these aspects, you can gain insight into whether you are underweight and take appropriate steps towards maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
Understanding Underweight
Definition of underweight
Underweight is a term used to describe a condition in which a person has a body weight that is considered below the normal or healthy range for their height, age, and sex. It is typically determined by calculating the Body Mass Index (BMI), which takes into account both weight and height. Being underweight can have various implications for overall health and well-being.
Significance of maintaining a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is vital for overall health and well-being. It plays a significant role in ensuring that the body functions optimally and can perform its daily activities effectively. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight helps to reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. It also supports a strong immune system, improves energy levels, and promotes better mental health.
Potential health risks of being underweight
Being underweight can pose various health risks and complications. Individuals who are underweight may have a weakened immune system, making them more susceptible to infections and illnesses. They may also experience nutrient deficiencies, which can lead to weakened bones, muscle weakness, and impaired growth and development. Additionally, underweight individuals may have an increased risk of complications during surgery and may experience fertility issues.
Factors contributing to being underweight
There are several factors that can contribute to being underweight. Some individuals may have a naturally higher metabolism, meaning they burn calories at a faster rate and may struggle to gain weight. Chronic illnesses, such as gastrointestinal disorders, hyperthyroidism, and eating disorders like anorexia nervosa, can also result in being underweight. Additionally, certain medications, genetic factors, and socioeconomic factors can influence a person’s weight status.
Calculating Body Mass Index (BMI)
Importance of BMI in determining underweight
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a useful tool in assessing whether an individual is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. It provides a standardized method of measuring body weight relative to height and is widely used in medical and health fields. By calculating BMI, healthcare professionals can evaluate an individual’s weight status and determine if it falls within a healthy range.
BMI formula
The BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. The formula for BMI is as follows:
BMI = (weight in kilograms) / (height in meters)²
Interpreting BMI results
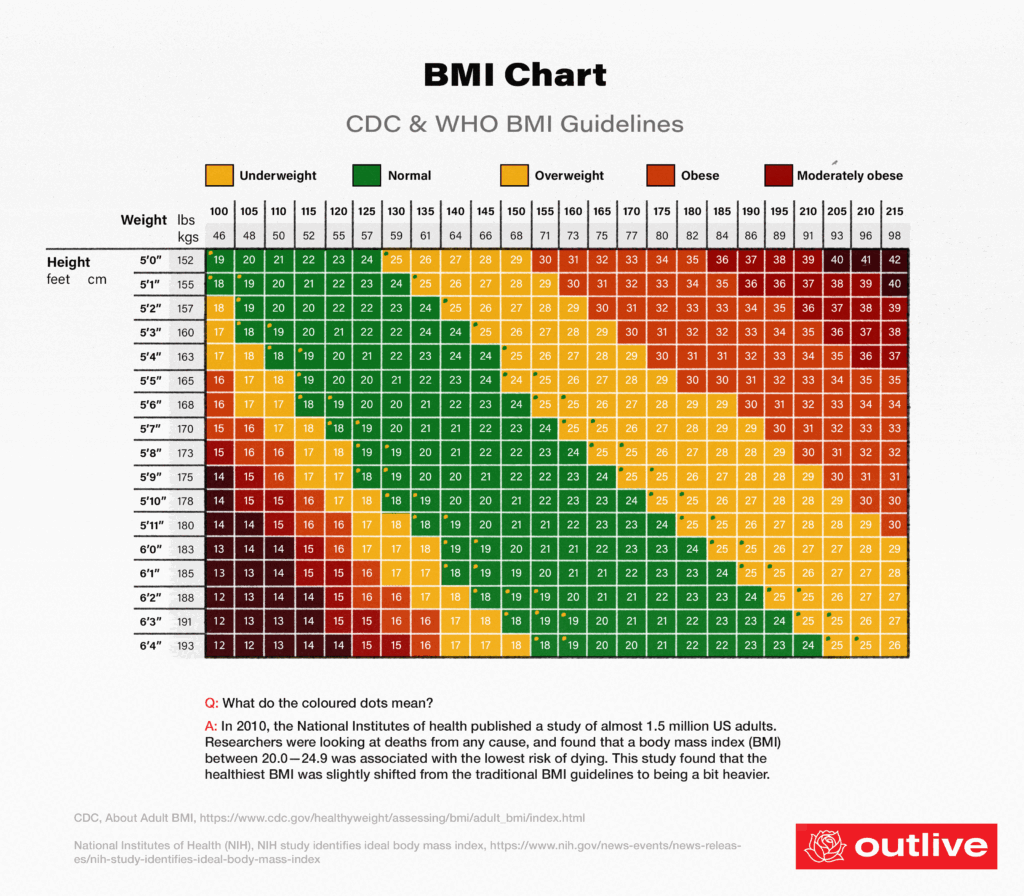
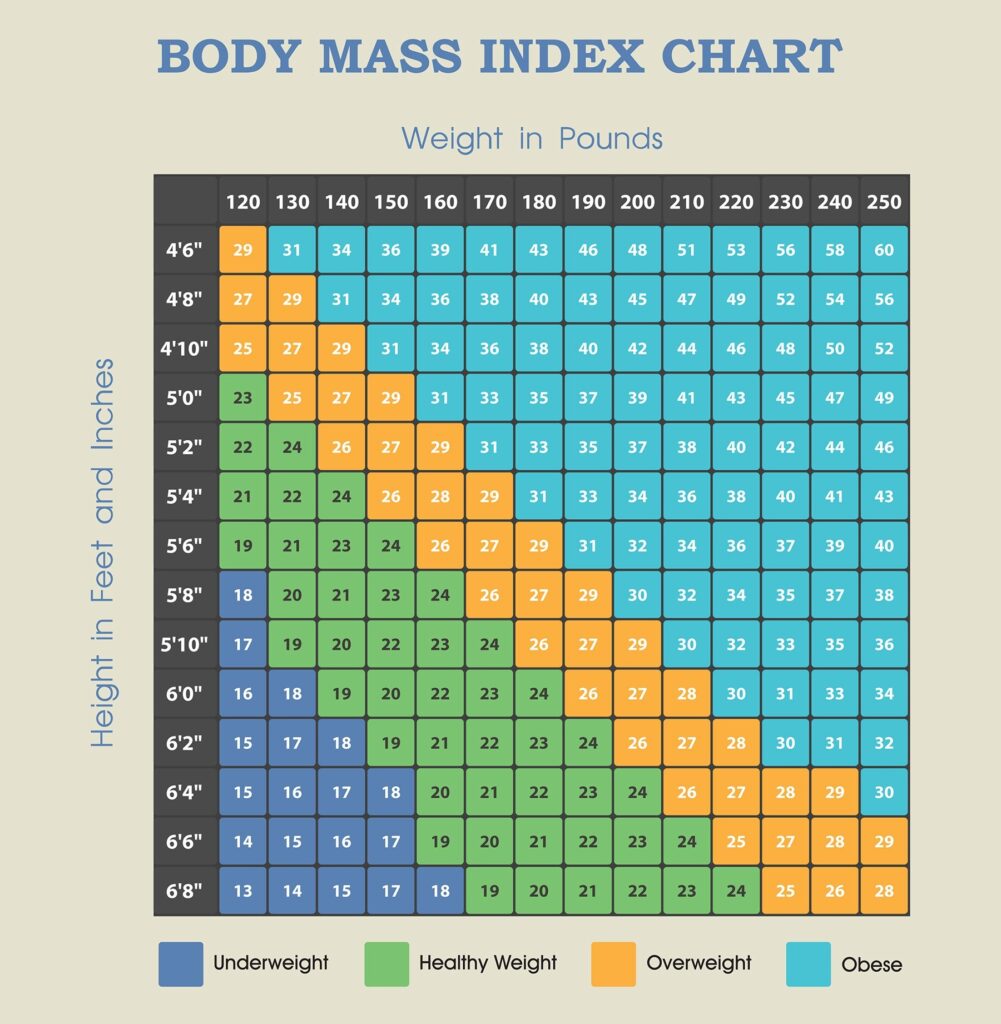
After calculating BMI, the results are interpreted using standard BMI categories. These categories include underweight (BMI less than 18.5), normal weight (BMI between 18.5 and 24.9), overweight (BMI between 25 and 29.9), and obese (BMI of 30 or higher). For the purpose of determining underweight, an individual would fall into the underweight category if their BMI is less than 18.5.
Limitations of using BMI alone
While BMI is a useful tool, it does have its limitations. It does not take into account factors such as muscle mass, bone density, and distribution of fat. This means that individuals with a higher percentage of muscle mass, such as athletes, may have a higher BMI despite being healthy and fit. Additionally, BMI does not consider other important factors such as body composition and overall health. Therefore, it is essential to consider other indicators and consult with healthcare professionals for a more comprehensive assessment.
Assessing Physical Appearance
Visual signs of being underweight
Visual signs can help in assessing whether someone is underweight. These may include visible bones, such as the ribs, shoulder blades, and collarbones, being more prominent due to low body fat and muscle mass. The face may appear gaunt, with hollowed cheeks and sunken eyes. The abdomen may look concave, and the individual may have an overall frail and thin appearance.
Observing body shape and structure
The body shape and structure can also provide clues about someone’s weight status. Underweight individuals may have a slender frame and lack the curves commonly associated with a healthy weight. Their arms and legs may appear thin and lack muscle tone, and their overall body proportions may appear unbalanced.
Identifying prominent bones
One noticeable sign of being underweight is the visibility of bones that are typically more hidden in individuals with a healthy weight. Prominent collarbones, hip bones, and spinal bones may be visible, indicating a lack of body fat covering these areas. While everyone’s bone structure is different, a noticeably thin or bony appearance can be an indicator of being underweight.
Noting overall frailty
A general observation of an individual’s physical appearance can help in determining if they are underweight. Underweight individuals may exhibit an overall frailty, with their bodies appearing delicate and lacking in muscle mass or body fat. They may have little to no muscle definition and appear physically weak.
Considering Health Symptoms
Lack of energy and persistent fatigue
A common symptom experienced by underweight individuals is a lack of energy and persistent fatigue. This can be due to a lack of sufficient calorie intake to meet the body’s energy needs. The body relies on calories from food to provide energy for daily activities and bodily functions. When someone is underweight, they may not be consuming enough calories to fuel their body adequately, resulting in feelings of tiredness and low energy levels.
Weakened immune system and frequent illnesses
Being underweight can weaken the immune system and make individuals more susceptible to frequent illnesses and infections. The body requires the proper nutrients and energy to support a robust immune system. When someone is underweight, their body may not have the necessary resources to fight off viruses and bacteria effectively, leading to an increased risk of getting sick.
Irregular menstrual cycle in females
For females, being underweight can disrupt the regular menstrual cycle. Insufficient calorie intake and low body weight can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to irregular periods or the absence of menstruation altogether. This can have potential long-term implications for reproductive health and fertility.
Difficulty in maintaining body temperature
Underweight individuals may experience difficulty in maintaining a stable body temperature. Adequate body fat acts as insulation and helps to regulate body temperature. Insufficient body fat can result in a decreased ability to retain heat, making underweight individuals more susceptible to feeling cold and uncomfortable even in moderate temperatures.

Using Weight and Height Measurements
Utilizing weight scales for assessment
Weight scales are commonly used to measure body weight and can be a helpful tool in determining if someone is underweight. Regularly weighing yourself and keeping track of any significant weight changes can provide insight into your weight status. However, it is important to note that weight alone does not provide a complete picture of overall health and should be considered alongside other factors.
Measuring height accurately
Accurate height measurement is crucial in calculating BMI and assessing weight status. Using a wall-mounted ruler or height measurement device, stand with your back against the wall, heels together, and head aligned. Ensure your heels, buttocks, and shoulders are touching the wall, and have someone mark the highest point on your head. Measure the distance between the floor and the mark to determine your height accurately.
Calculating body mass index (BMI) using measurements
Once you have obtained your weight and height measurements, you can calculate your BMI using the formula mentioned earlier. Divide your weight in kilograms by the square of your height in meters, and you will obtain your BMI.
Determining if BMI falls within underweight range
Compare your calculated BMI to the underweight category, which is a BMI less than 18.5. If your BMI falls within this range, it suggests that you may be underweight. However, it is important to remember that BMI is just one tool, and it is essential to consider other factors, such as overall health and personal circumstances.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Importance of professional medical advice
Seeking professional medical advice is crucial when assessing whether you are underweight. Healthcare professionals have the knowledge and expertise to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of your health status and provide personalized recommendations for achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
Scheduling an appointment with a doctor
To get a thorough assessment of your weight status and address any concerns, it is advisable to schedule an appointment with a doctor. They can conduct a physical examination, review your medical history, and perform any necessary tests to determine if you are underweight and if any underlying conditions contribute to your weight status.
Discussing concerns and symptoms
During your appointment, it is important to openly discuss your concerns and any symptoms you may be experiencing. This will help the doctor gain a better understanding of your situation and guide them in providing appropriate advice and treatment options based on your specific needs.
Seeking guidance for healthy weight management
Healthcare professionals can provide valuable guidance for healthy weight management. They can tailor a personalized plan that includes dietary recommendations, exercise guidelines, and lifestyle modifications to help you achieve a healthy weight. It is important to follow their advice and maintain regular communication to ensure ongoing support and monitor your progress.
Assessing Eating Habits
Recognizing restricted food intake
Restricted food intake, such as consistently eating insufficient calories or avoiding certain food groups, can contribute to being underweight. This can be due to various factors, including disordered eating patterns, restrictive diets, and inadequate appetite. Recognizing any patterns of restricted food intake can help identify potential causes of being underweight.
Noting loss of appetite
A loss of appetite can significantly impact an individual’s ability to consume an adequate amount of calories and nutrients. Underlying factors such as stress, medication side effects, or certain medical conditions can contribute to a decreased appetite. Noting any changes in appetite and discussing them with a healthcare professional can help identify potential reasons for being underweight.
Identifying unintentional weight loss
Unintentional weight loss is a significant indicator of being underweight. If you have noticed a substantial decrease in your weight without actively trying to lose weight, it may be a cause for concern. Identifying unintentional weight loss and discussing it with a healthcare professional is vital to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate management plan.
Understanding disordered eating patterns
Disordered eating patterns, such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia, can lead to being underweight. These eating disorders are characterized by unhealthy relationships with food, distorted body image, and extreme food restriction or purging behaviors. Recognizing disordered eating patterns and seeking professional help is crucial for both physical and mental well-being.
Examining Psychological Factors
Understanding body image perception
Body image perception plays a significant role in one’s perception of their weight and overall appearance. Distorted body image can lead to a preoccupation with weight loss or constant dissatisfaction with one’s body, even when they are underweight. Understanding body image perception can provide insight into potential psychological factors contributing to being underweight.
Recognizing signs of body dysmorphia
Body dysmorphia is a mental health condition characterized by a persistent and excessive preoccupation with perceived flaws in one’s appearance. Individuals with body dysmorphia tend to have distorted perceptions of their body size, shape, and weight, often obsessing over perceived imperfections. Recognizing signs of body dysmorphia can help identify psychological factors underlying being underweight.
Exploring underlying psychological conditions
Various underlying psychological conditions can contribute to unhealthy weight and being underweight. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and stress can affect appetite, self-esteem, and overall well-being. Exploring underlying psychological conditions and seeking professional help can be essential in managing and treating underweight related to psychological factors.
Identifying stress-related weight loss
Stress can significantly impact appetite and weight. High stress levels can lead to decreased food intake and unintentional weight loss. Understanding the relationship between stress and weight loss can help identify stress-related factors contributing to being underweight and allow for appropriate interventions and support.
Comparing with Healthy Weight Range
Knowing the healthy weight range for your height
Understanding the healthy weight range for your unique height is an important consideration when assessing if you are underweight. The healthy weight range varies based on factors such as gender, body type, and muscle mass. Consulting resources or healthcare professionals can help you determine the healthy weight range specific to your individual circumstances.
Determining if current weight falls within healthy range
By comparing your current weight to the healthy weight range for your height, you can identify if you fall within the range considered to be healthy. If your weight falls below the lower end of the healthy weight range, it suggests that you may be underweight. This information can be valuable when seeking professional guidance for managing weight goals.
Considering individual variations and body types
It is important to consider individual variations and body types when assessing if you are underweight. Everybody is unique, and factors such as genetics, muscle mass, and bone structure can influence weight and body composition. A comprehensive evaluation should take these factors into account to ensure a more accurate assessment.
Seeking professional guidance for weight goals
If you suspect you are underweight or have identified that you are below the healthy weight range for your height, seeking professional guidance is crucial. Healthcare professionals can help determine appropriate weight goals based on your individual circumstances, taking into account factors such as overall health, lifestyle, and personal preferences.
Evaluating Overall Well-being
Considering overall health and vitality
When assessing whether you are underweight, it is important to consider your overall health and vitality. Evaluate how you feel physically and mentally, taking note of any symptoms or limitations you may be experiencing. A holistic assessment of your well-being can provide valuable insights into the potential impact of being underweight on your daily life.
Assessing physical and mental functioning
Consider how being underweight may be impacting your physical and mental functioning. Are you experiencing decreased energy levels, difficulty concentrating, or changes in your mood? Assessing physical and mental functioning can help identify areas that may require intervention or support.
Understanding the impact of underweight on daily life
Underweight individuals may face various challenges in their daily lives. Physical limitations, decreased immune function, and mental health concerns can impact overall quality of life. Understanding the specific ways in which being underweight affects your daily life can help you seek appropriate assistance and support.
Identifying the need for intervention and support
Finally, evaluating if you are underweight involves identifying the need for intervention and support. If you suspect you are underweight and are experiencing negative symptoms or impacts on your well-being, it is important to seek help. Healthcare professionals, nutritionists, and mental health specialists can provide the necessary guidance and support to help you address and manage any underlying issues associated with being underweight.
In conclusion, understanding underweight involves considering various factors, including BMI, physical appearance, health symptoms, weight and height measurements, psychological factors, and overall well-being. It is essential to take a holistic approach and seek professional guidance when assessing if you are underweight. Remember to prioritize your health and well-being above all else and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and support.